Pediatric Cardiology

PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
pediatric Cardiology is a specialized branch of medicine that deals with diagnosing and treating heart problems in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatric cardiologists are trained to manage complex and high-risk conditions involving the heart and circulatory system from the fetal period through young adulthood.This specialty covers a wide range of conditions, including congenital heart defects (heart abnormalities present at birth), arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and acquired heart diseases that develop during childhood. Pediatric cardiologists work closely with pediatric cardiac surgeons to plan and coordinate care for patients needing surgical interventions.Key aspects of Pediatric Cardiology include:
These are structural problems with the heart that are present from birth, ranging from simple defects with no symptom to complex abnormalities with severe, life-threatening symptoms
Conditions like rheumatic heart disease, Kawasaki disease,and infective endocarditis, which can affect children’s heart health.Rheumatic heart disease stems from untreated strep throat infections, leading to heart valve damage. Kawasaki disease causes inflammation in blood vessels, potentially resulting in coronary artery aneurysms. Infective endocarditis, often bacterial, affects the heart’s inner lining and valves.
Advanced imaging techniques, including echocardiography, MRI, and CT scans, to visualize the heart and blood vessels, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.Echocardiography utilizes ultrasound to produce real-time images of the heart’s structure and function, aiding in the assessment of cardiac function, valve abnormalities, and congenital defects. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers detailed, non-invasive visualization of cardiac anatomy and function, particularly useful for assessing myocardial viability and detecting structural abnormalities.
Specialized care that focuses on detecting heart defects before birth and planning for the care of the baby after delivery.Using advanced imaging techniques such as fetal echocardiography, specialists can assess the structure and function of the fetal heart in utero. This enables early detection of congenital heart defects, rhythm abnormalities, and other cardiac issues, allowing for timely intervention and treatment planning.
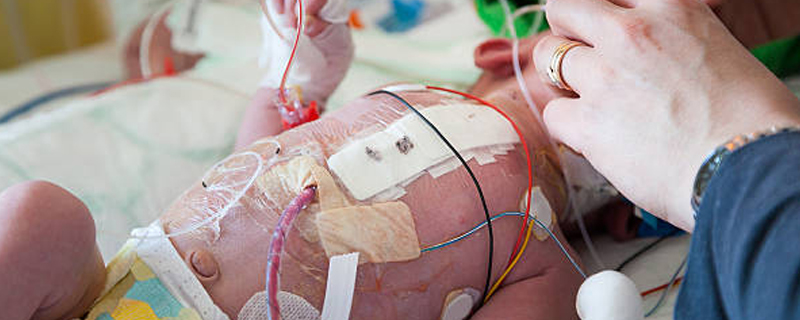
Procedures performed through catheters inserted into the blood vessels,avoiding the need for open-heart surgery. These can include balloon angioplasty, stent placement, and closure of some types of heart defects.
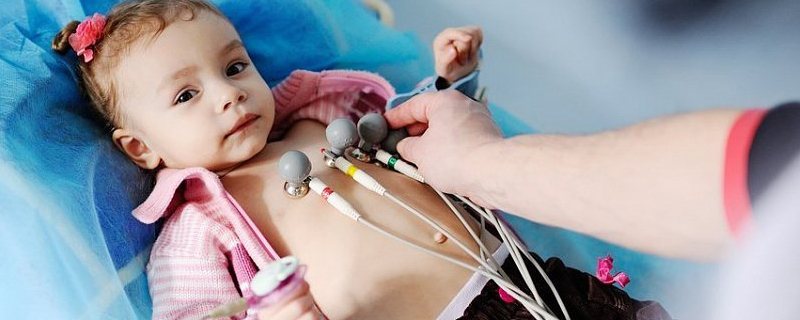
Diagnosis and treatment of heart rhythm disorders, including the use of pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs)
