Nephrology

Nephrology
Nephrology is a specialty of medicine that focuses on the study, diagnosis, and treatment of kidney functions and diseases. Nephrologists are medical doctors who specialize in kidney care and treating diseases of the kidneys.The kidneys are vital organs that perform many crucial functions, including filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood, which are then excreted in the urine. They also play an important role in regulating blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell production.
A long-term condition characterized by a gradual loss of kidney function over time.This can result in a buildup of waste products and fluids in the body, leading to various complications such as electrolyte imbalances, high blood pressure, anemia, bone disease, and cardiovascular problems. Management of CKD typically involves lifestyle modifications, medication, and, in advanced stages, renal replacement therapy such as dialysis or kidney transplantation
A sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or days. AKI is characterized by a sudden and rapid decline in kidney function, leading to a buildup of waste products and fluids in the body. This condition can occur within a few hours or days and is often reversible with prompt medical intervention. Common causes of AKI include severe infections, dehydration, reduced blood flow to the kidneys (such as from shock or surgery), certain medications, and kidney damage from toxins or injury. Treatment involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause, along with supportive measures to help restore kidney function and prevent complications.
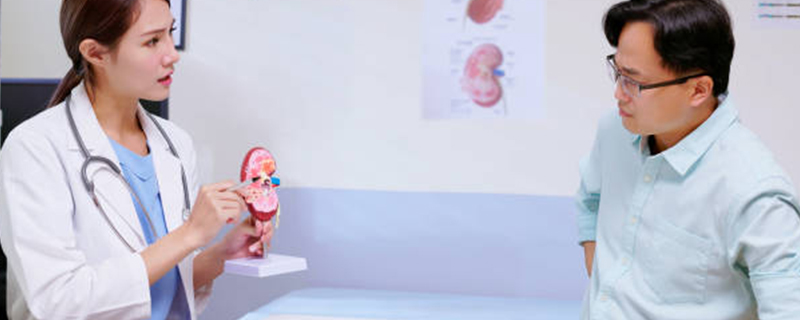
A group of diseases that cause inflammation and damage to the kidney’s filtering units.Glomerulonephritis can result from various causes, including autoimmune disorders, infections, medications, and systemic diseases. Common symptoms include hematuria (blood in the urine), proteinuria (protein in the urine), hypertension, and decreased kidney function.
Solid masses made of crystals that originate in the kidneys but can affect any part of the urinary tract. including the ureters, bladder, and urethra. Kidney stones can vary in size and composition, with common types including calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, and struvite stones. Symptoms of kidney stones may include severe pain in the back or side, blood in the urine, difficulty urinating, and nausea/vomiting
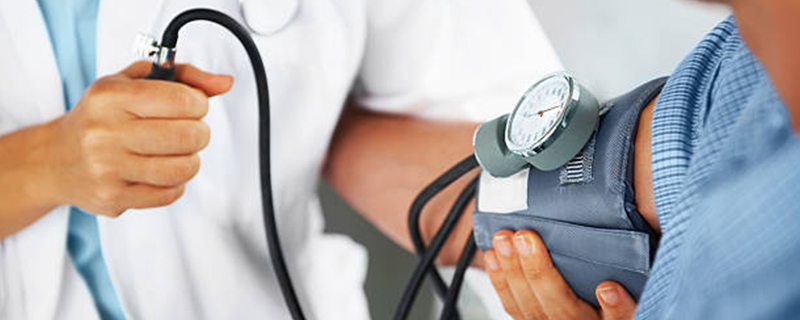
Managed as it is closely related to kidney health and can lead to kidney damage if not controlled. hypertension can lead to kidney damage over time, as the high pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys and impair their function.
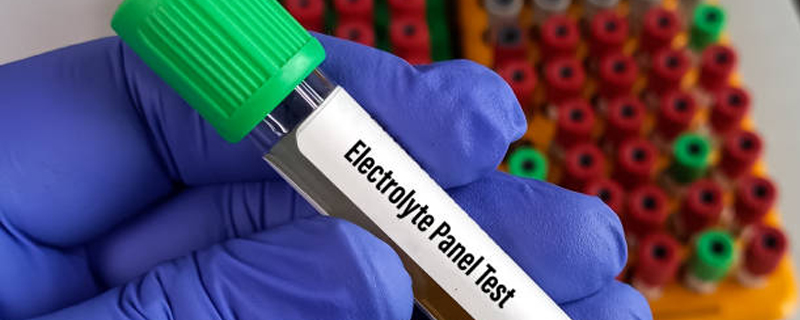
Imbalances in the body’s levels of sodium, potassium, and other key electrolytes.Electrolytes play crucial roles in various bodily functions, including nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and fluid balance. Imbalances can result from conditions such as dehydration, kidney disorders, hormonal imbalances, medications, or certain diseases. Symptoms of electrolyte imbalances may include weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, confusion, and seizures.
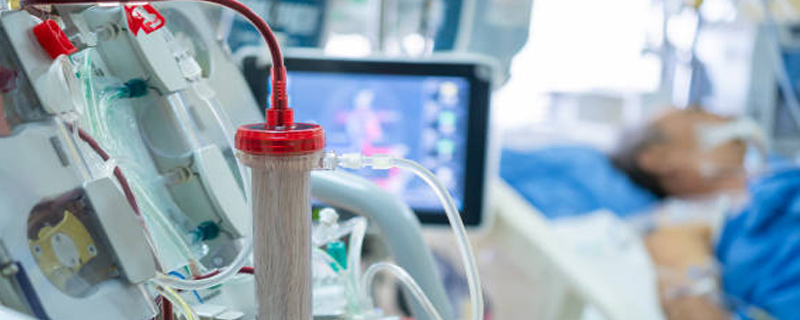
Including dialysis and kidney transplantation for patients with end-stage renal disease.Dialysis involves the use of a machine to filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys are no longer able to perform this function adequately. Kidney transplantation is a surgical procedure where a healthy kidney from a donor is transplanted into the recipient’s body to replace the failed kidneys.
