Pediatric Neurology

Pediatric Neurology
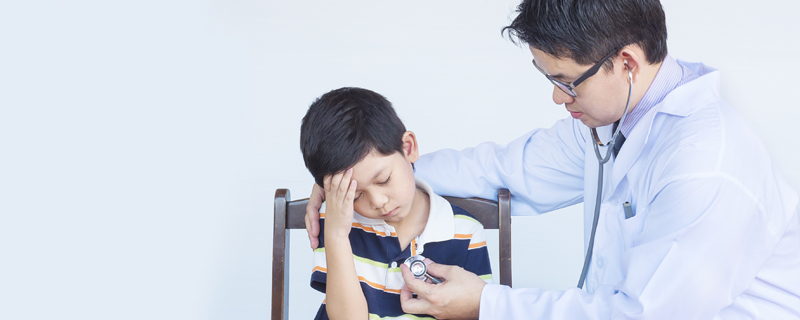
Pediatric Cardiology is a specialized branch of medicine that deals with diagnosing and treating heart problems in infants, children,and adolescents. Pediatric cardiologists are trained to manage complexand high-risk conditions involving the heart and circulatory system from the fetal period through young adulthood.
This specialty covers a wide range of conditions, including congenital heart defects (heart abnormalities present at birth), arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and acquired heart diseases that develop duringchildhood. Pediatric cardiologists work closely with pediatric cardiac surgeons to plan and coordinate care for patients needing surgical interventions.Key aspects of Pediatric Cardiology include:
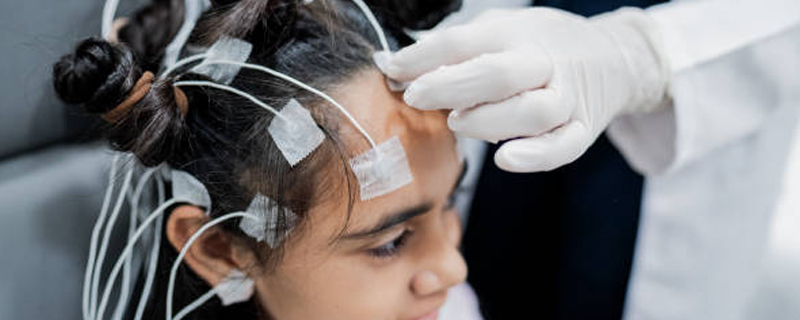
Management and treatment of various types of seizures and epilepsy syndromes.Epilepsy and seizure disorders encompass a range of conditions characterized by abnormal electrical activity in the brain, leading to seizure

Including autism spectrum disorder(ASD) and ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder), focusing on their neurological aspects.
ASD involves challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors, while ADHD is marked by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Understanding their neurological aspects aids in developing targeted interventions and support strategies.
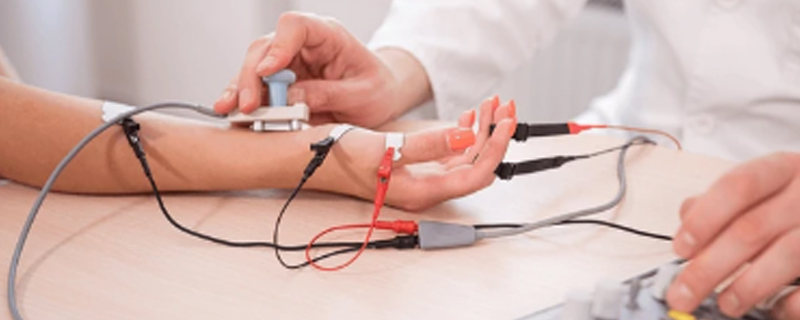
Such as muscular dystrophy and nerve-muscle disorders like Charcot-Marie Tooth disease.Neuromuscular disorders encompass a broad range of conditions affecting the nerves that control voluntary muscles. These disorders can lead to symptoms such as muscle weakness, numbness, cramps, and fatigue. Examples include muscular dystrophy, ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), myasthenia gravis, and neuropathies.

Managing movement disorders that arise from brain damage.cerebral palsy is a group of neurological disorders affecting movement and posture,often caused by brain damage during early development.
These are structural problems with the heart that are present from birth, ranging from simple defects with no symptoms to complex abnormalities with severe, life-threatening symptoms.

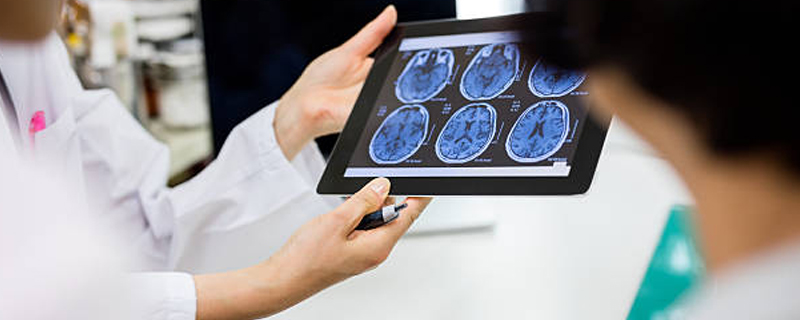
Diagnosis and treatment planning for neurological aspects of brain tumors.Headaches and migraines are common neurological disorders characterized by recurrent pain in the head. While headaches can vary in intensity and cause, migraines typically involve severe throbbing pain, often accompanied by other symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound

Comprehensive care for chronic headaches and migraines.Neurogenetic disorders are conditions caused by abnormalities in the genes that affect the development or functioning of the nervous system. Examples include Huntington’s disease, muscular dystrophies, and certain types of epilepsy. These disorders often have a genetic component and can lead to a wide range of neurological symptoms and impairments
Such as spina bifida and brain malformations.Pediatric neurologists employ a variety of diagnostic tools, including EEG (Electroencephalogram) for studying brain activity, MRI and CT scans for detailed imaging, and lumbar punctures for examining the cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment approaches can range from medications and lifestyle changes to support neurological health, to therapies for improving function and reducing symptoms, and in some cases,surgery.By focusing on the unique needs of children with neurological conditions, pediatric neurologists play a crucial role in helping them achieve their fullest potential, improving their quality of life, and supporting their families through diagnosis, treatment, and beyond.
